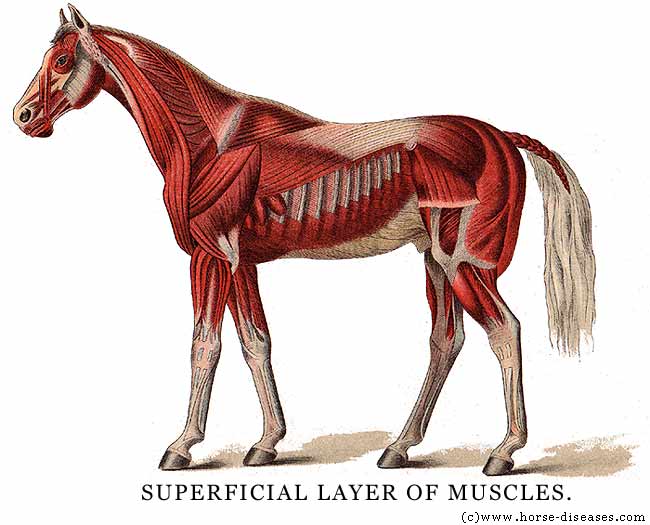
Horse muscle anatomy
The horse's musculoskeletal system consists of the bones, cartilage, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Their primary function is to support of the body, provide motion, and protect vital organs. There are 205 bones in the horse's skeleton. Twenty of these bones are in each foreleg and 20 in each hind limb, for a grand total of 80 bones in.

Horse anatomy, Horse behavior, Horses
Anatomy. The Iliopsoas muscle group is comprised of the Psoas Major and the Iliacus muscle. Psoas Major.. Rock, S. (2012) Anatomy of the Horse. Posted by Vet Physio Phyle November 12, 2018 October 30, 2020 Posted in Uncategorized Tags: muscle Post navigation. Previous Post Previous post: Persevering through physical illness. Next Post Next.
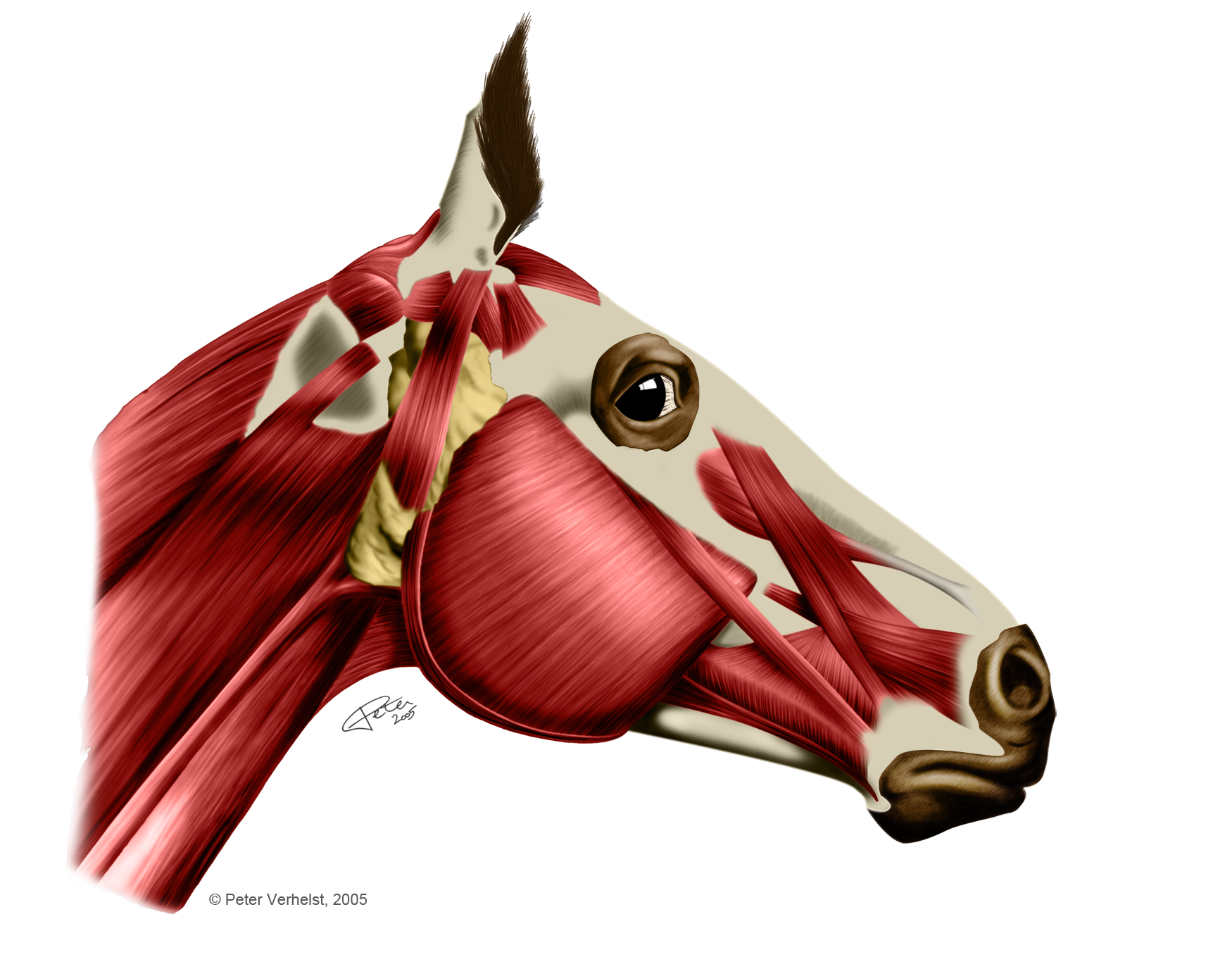
Muscles of a horse head by PeterAndTheWolf on DeviantArt
Types of muscle. There are 3 types of muscle, all found within the equine: Skeletal muscle: Contraction of these muscles leads to the muscle pulling a tendon, which in turn pulls a bone. Moving a bone results in either flexing or extending a joint.
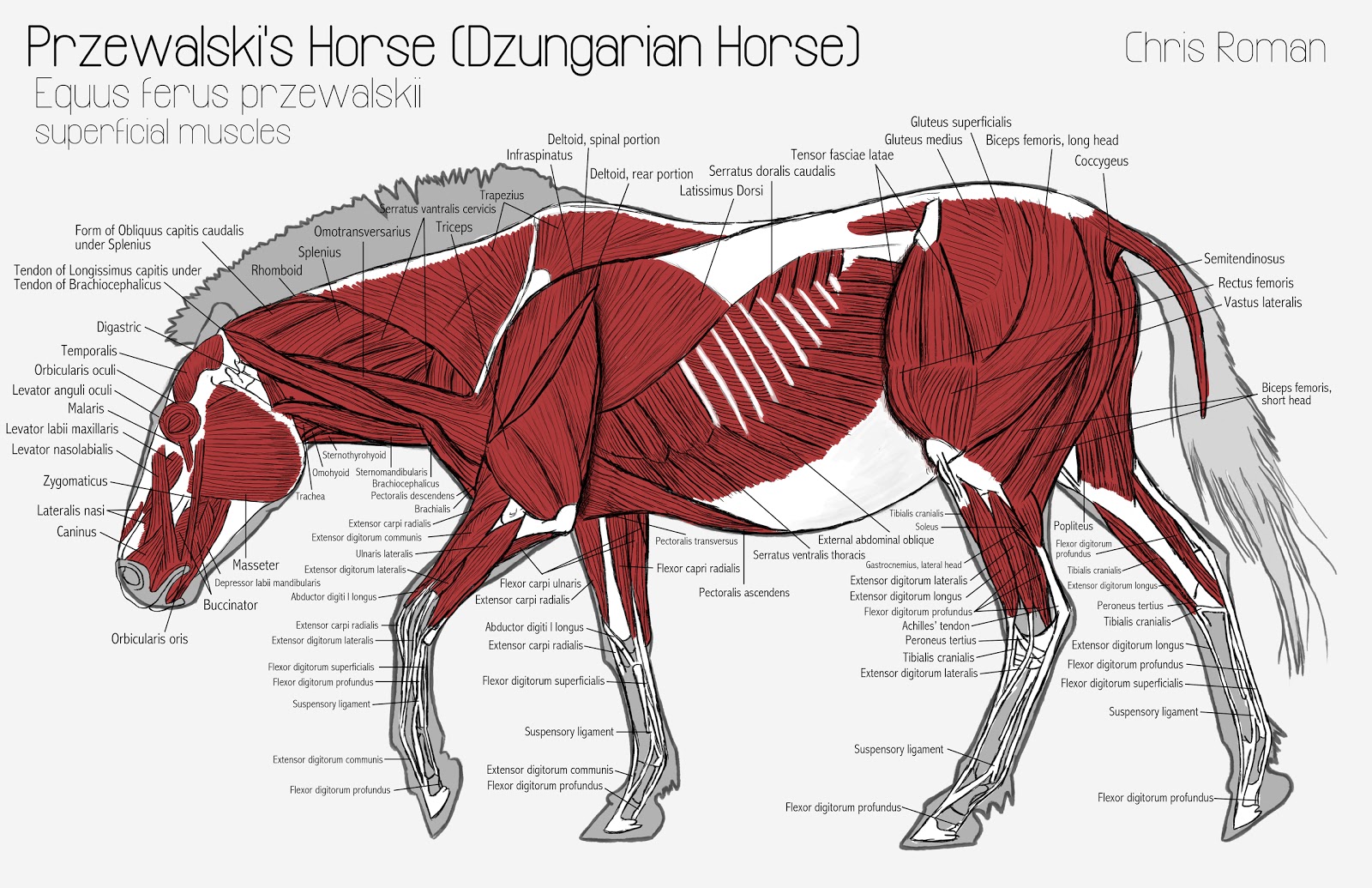
Chris Roman Horse Anatomy Study
Here, I will show you some of the important muscles of the horse body. If possible, I will add some other horse muscle pictures in the future. Horse anatomy digestive system. You will find many peculiar characteristics in the horse anatomy digestive system. I will provide some peculiar anatomical features from the horse's digestive system.

horse anatomy model Google Search Horse anatomy, Horse health, Horses
Dr Christin Finn, DVM, CVA details the underlying skeleton and muscle structure of a horse by using a live painted horse Find more information about your hor.

Full color poster of the equine deep muscular system. Perfect for a
19. Understanding how muscles work is one of the most fundamental concepts that can influence how we ride and train our horses. Movement is created by the skeletal muscles pulling on the bones to operate the joints. Every bone is moved by a muscle. The muscles cross either one joint or several. The longissimus dorsi.

120 best images about Horse anatomy and physiology on Pinterest
Tibia. Large and only weight bearing component of crus (stifle/ knee) Large tibial tuberosity - patellar ligament. Medial tibia is subcutaneous. Cochlea is inclined craniolaterally. This causes the lower limb to move laterally on flexion. Fibula is greatly reduced. Distally incorporated into tibia. Proximally tightly articulated with tibia.

Muscle Anatomy Of The Horse In Antique Engraving Stock Vector Art
Wing of atlas and mastoid process of temporal bone. Elevates head and neck. Bends head and neck laterally. Stabilizes and extends vertebral column. Dorsal branch of local spinal nerve. M. Semispinalis capitis. Articular processes of C2/3-7 and transverse processes of T1-6/7. Occipital bone. Elevates head and neck.

Pin on Equine Anatomy
Points of a horse. Equine anatomy encompasses the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses,. the tongue and related muscles, the cheeks and the lips. Horses also have three pairs of salivary glands, the parotoid (largest salivary gland and located near the poll), mandibular (located in the jaw), and sublingual (located under the tongue).

Image result for horse muscles diagram Horse anatomy, Horses, Horse
Tendons are tough bands of connective tissue made up mostly of a protein called collagen. They stretch very little. Tendons attach each end of a muscle to a bone. At selected points, they are located within sheaths that allow them to move easily. Ligaments are also tough cords formed of connective tissue.

Horse Muscular Anatomy Poster
Abscess - An infection of the sensitive tissues of the hoof. Cause: Rocks, deep bruising of the sole, nails, and/or sharp objects that puncture sensitive tissue of the hoof. Abscesses will follow the path of least resistance. Sometimes puncture hole may be seen (black spot). The leg may be hot and swollen. Call a vet if not experienced!
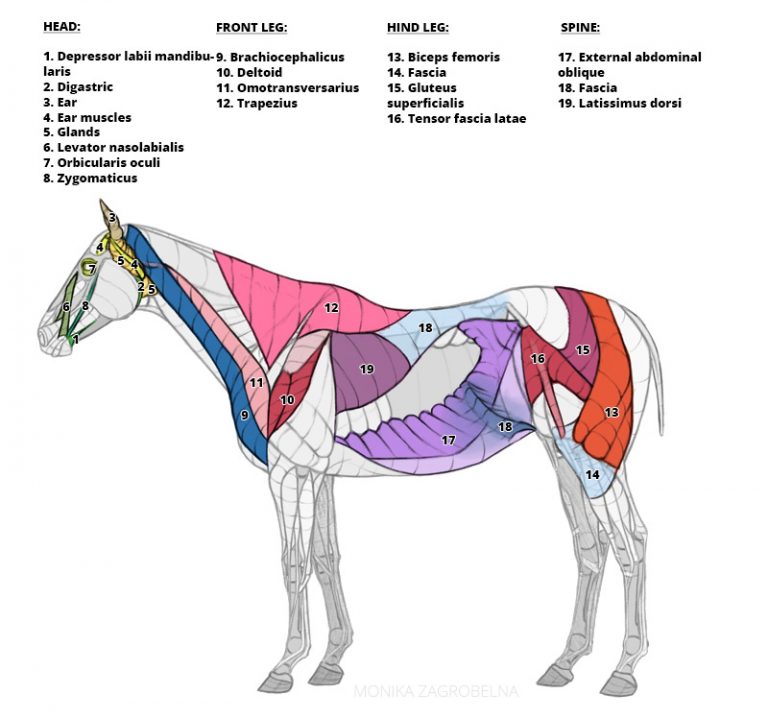
Horse Anatomy for Artists Skeleton and Muscle Diagrams Monika Zagrobelna
Horse Anatomy and Muscle Diagrams. This page contains color coded pictures of the horse's deep, superficial and hind end muscles.. Like humans, all horses need to have their muscles stretched to prevent injury and improve their comfort and performance level. We created this 25 video collection to teach you how to safely and correctly do this!

Superficial Front Limb & Neck Muscles, Front View Equine Massage
Head and Neck - Horse Muscle Anatomy. The muscles of the head and neck allow the horse to flex, extend and tilt its head. Key muscles include: Temporalis - raises the jaw. Masseter - closes the jaw. Sternomandibularis - opens the mouth by lowering the jaw. Brachiocephalicus - flexes the head and neck; turns the head side to side.

Anatomy of the horse The shoulder Animal Osteo Louise Mauferon
Horse muscle anatomy chart Horse anatomy skeleton Horse head. The horse's head is quite heavy - it can weigh approximately 16 kg if the horse is big. You should remember about this, especially when you allow the horse to "hang" on a bit and you "carry" his head's weight with your arms throughout the whole ride by holding the reins. After an.
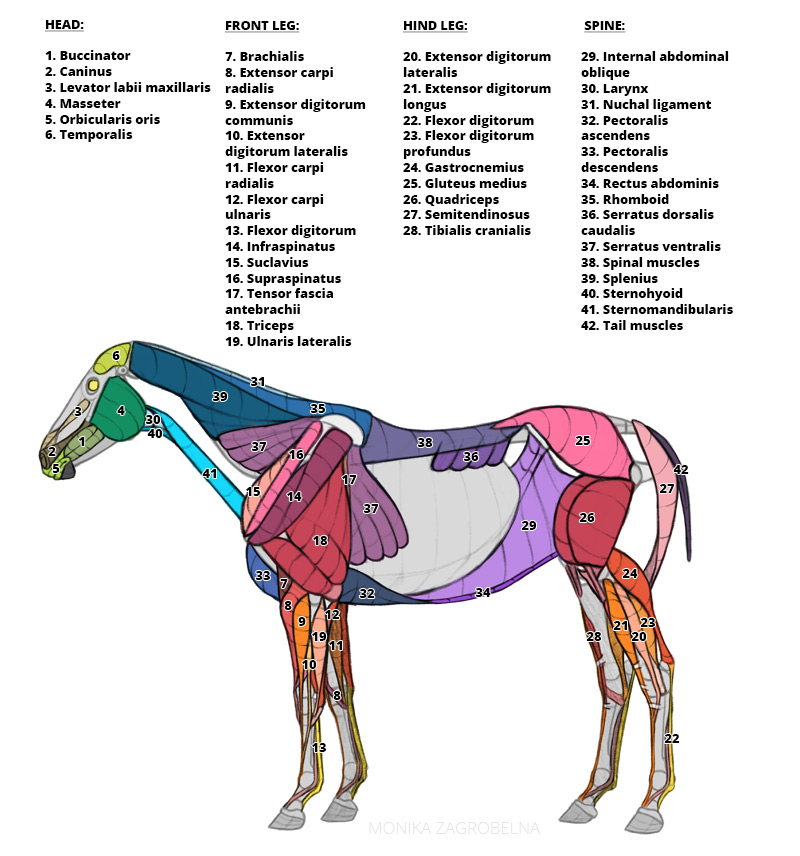
Horse Anatomy for Artists Skeleton and Muscle Diagrams Monika Zagrobelna
The Equine Muscular System. The muscles of the body are responsible for creating movement whether it be via the skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, or cardiac muscle. Agonist muscles contract and are the primary mover. While antagonist muscles work by counteracting the agonist muscle therefore creating a balanced and stable movement.
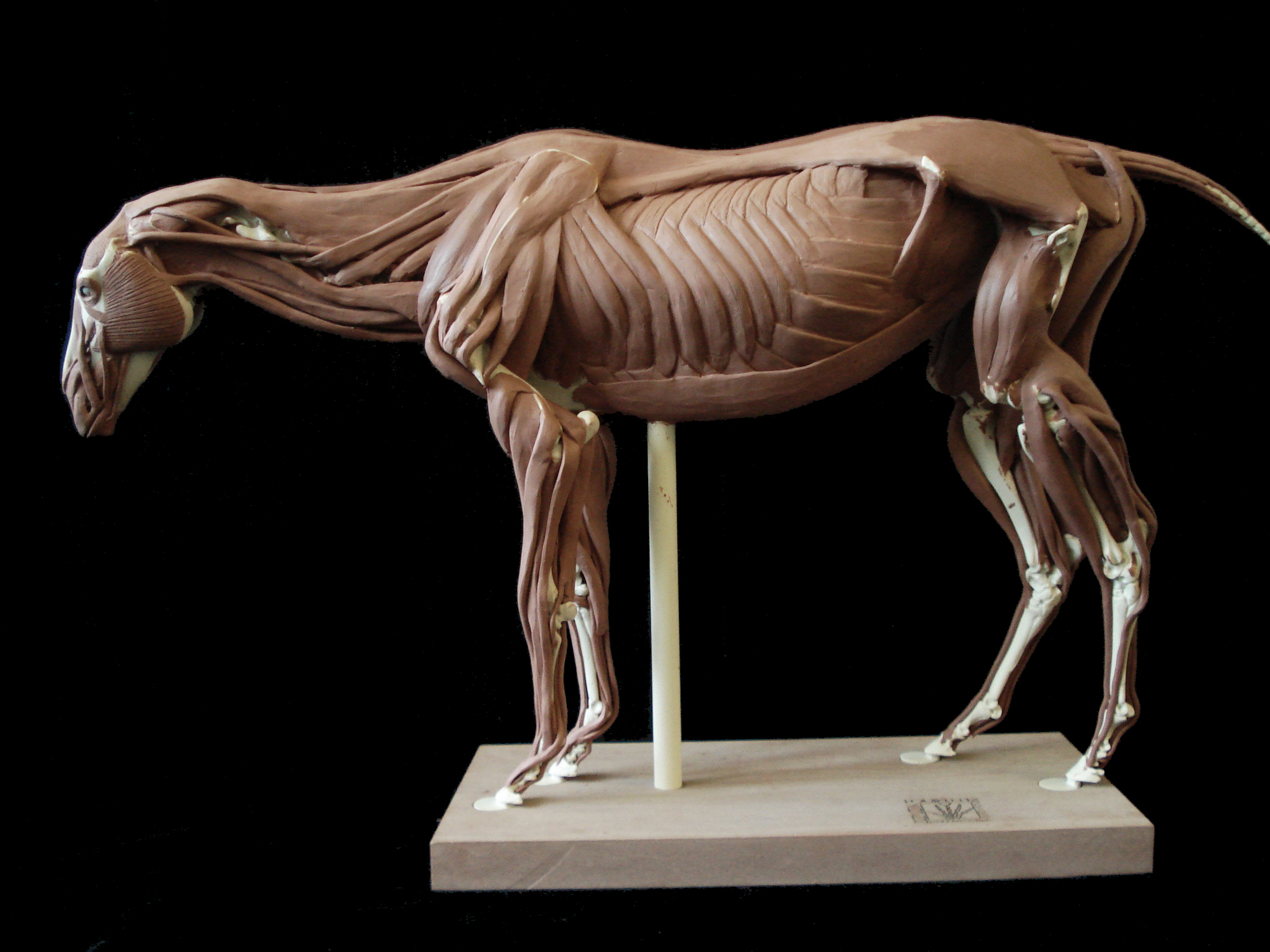

horse anatomy on Pinterest Animal Anatomy, Horses and Anatomy
The top line is a horse muscle anatomy term that describes the coverage of the horse trapezius muscle, neck, back withers, loin, and coup. Horses with a muscular topline will be stronger and more athletic than those without one. Protein is a natural horse muscle supplement and one of the best horse supplements for muscle gain.